Landmark Placement: Mission Location Identification Using Map Features

Landmark placement, leveraging map features, is crucial for identifying potential mission locations by providing a tangible reference point, aiding in navigation, situational awareness, and strategic decision-making.
When planning a mission, the ability to pinpoint the most suitable locations is crucial. Landmark placement using map features offers a robust method for identifying potential mission spots, enhancing navigation, and improving overall mission success. Let’s explore how this works.
Understanding the Basics of Landmark Placement
Landmark placement, in the context of mission planning and city & map analysis, refers to strategically using recognizable and distinct features on a map to identify potential locations for various operations. These landmarks serve as reference points that are easily identifiable, even in challenging conditions.
By understanding the principles of landmark placement, mission planners can create a more effective and reliable system for locating and utilizing key sites within a given area.
Why are Landmarks Important?
Landmarks play a crucial role in enhancing the accuracy and efficiency of mission planning. Here’s why:
- Improved Navigation: Landmarks act as visual aids, helping personnel navigate through unfamiliar territory with greater confidence.
- Enhanced Situational Awareness: By using well-defined landmarks, teams can better understand their surroundings and maintain accurate situational awareness.
- Effective Communication: Landmarks provide a common reference point for communication, ensuring that all team members are on the same page.
Landmarks are instrumental in coordinating movements, ensuring everyone knows exactly where they are and where they need to be.
The Role of Map Features in Location Identification
Map features form the backbone of landmark placement, offering a variety of distinct elements that can be used for location identification. Recognizing these features is essential for effective mission planning.
Map features can vary from natural landmarks to man-made structures, each offering unique opportunities for mission location spotting.
Types of Map Features
Understanding the different types of map features allows mission planners to choose the most appropriate landmarks for their needs:
- Natural Landmarks: These include rivers, mountains, forests, and distinctive rock formations.
- Man-Made Structures: Buildings, bridges, towers, and roads fall into this category.
- Topographic Features: Contour lines, elevation points, and slope gradients are essential for understanding terrain.
Combining these different types of map features can provide a comprehensive understanding of the mission environment.
Selecting the Right Landmarks: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right landmarks is crucial for ensuring mission success. Several factors need to be considered to make an informed decision.
Selecting landmarks isn’t just about picking prominent features; it’s about choosing reliable and consistent indicators.
Key Factors for Landmark Selection
When selecting landmarks, consider these crucial elements:
- Visibility: The landmark should be easily visible from multiple vantage points.
- Distinctiveness: It should have unique characteristics that differentiate it from its surroundings.
- Permanence: The landmark should be relatively permanent and not subject to frequent changes.
Always check if a landmark meets all three conditions to maximize its usefulness.
Utilizing Geographic Information Systems (GIS) for Landmark Placement
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) offer powerful tools for analyzing map features and optimizing landmark placement. GIS software can enhance the precision and effectiveness of mission planning.
GIS helps mission planners to identify, analyze, and visualize geographical data for better decision-making.
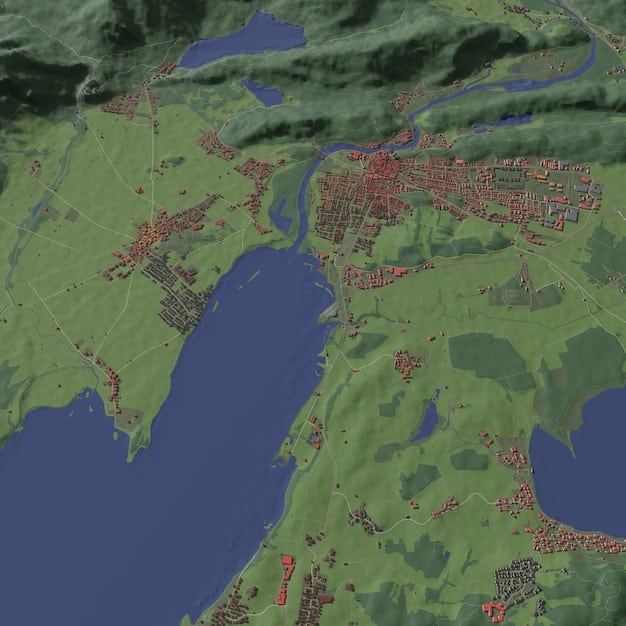
How GIS Enhances Landmark Placement
GIS tools provide several advantages:
- Data Integration: GIS can combine various data sources, such as satellite imagery, topographic maps, and street-level views.
- Spatial Analysis: Tools for analyzing spatial relationships, distances, and terrain characteristics.
- Visualization: GIS allows planners to visualize mission environments in 3D, enhancing their understanding of the terrain.
These capabilities enable precise and informed landmark placement, leading to more successful missions.
Case Studies: Successful Landmark Placement in Missions
To illustrate the effectiveness of landmark placement, let’s examine a few case studies where it has significantly contributed to mission success.
Real-world examples provide valuable insights into how landmark placement is applied in various scenarios.
Example Scenarios
Consider these hypothetical situations:
- Urban Search and Rescue: Using high-rise buildings and distinct street layouts as landmarks.
- Military Reconnaissance: Relying on natural terrain features and key infrastructure for navigation.
- Environmental Monitoring: Utilizing unique geological formations and water bodies to track changes.
Each case study demonstrates how careful landmark placement can lead to improved operational effectiveness.
Challenges and Mitigation Strategies in Landmark Placement
Despite its benefits, landmark placement is not without its challenges. Addressing these challenges proactively is key to ensuring mission success.
Potential issues include changing environments, reliability of data, and limitations in visibility.
Common Challenges
Here are some frequent challenges and strategies to mitigate them:
- Environmental Changes: Regularly update map data to reflect changes in the environment.
- Limited Visibility: Use multiple landmarks to compensate for obscured views.
- Data Inaccuracies: Cross-reference data from multiple sources and conduct ground truth verification.
Preparedness enhances the reliability of the landmarks used during mission planning.
| Key Aspect | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| 📌 Landmark Importance | Landmarks enhance navigation and situational awareness. |
| 🗺️ Map Features | Natural and man-made features aid in location identification. |
| ✅ Landmark Selection | Visibility, distinctiveness, and permanence are essential. |
| 🌐 GIS Utilization | GIS enhances precision and effectiveness in landmark placement. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
▼
In mission planning, a landmark is a recognizable or distinct feature on a map or in the environment that is used as a point of reference for navigation and situational awareness. Landmarks help in identifying locations and coordinating movements.
▼
Landmark placement is crucial because it enhances navigation accuracy, improves situational awareness, and facilitates clear communication among team members. This ultimately leads to more efficient and successful mission execution.
▼
GIS tools provide capabilities such as data integration, spatial analysis, and 3D visualization, which help mission planners identify suitable landmarks, analyze terrain, and understand spatial relationships with greater precision.
▼
Key considerations include selecting landmarks that are highly visible, distinct from their surroundings, and relatively permanent. Landmarks should be easily identifiable from multiple vantage points to ensure reliability.
▼
Challenges can include environmental changes affecting landscape visibility, limited visibility due to weather conditions or obstructions, and data inaccuracies in maps. Mitigation strategies involve regularly updating map data from multiple sources.
Conclusion
Effective landmark placement using map features is essential for identifying potential mission locations, greatly enhancing navigation, situational awareness, and overall mission success. By understanding the importance of landmarks, considering key factors for their selection, and leveraging GIS tools, mission planners can significantly improve their operations. Addressing potential challenges proactively ensures that missions are executed smoothly and efficiently.